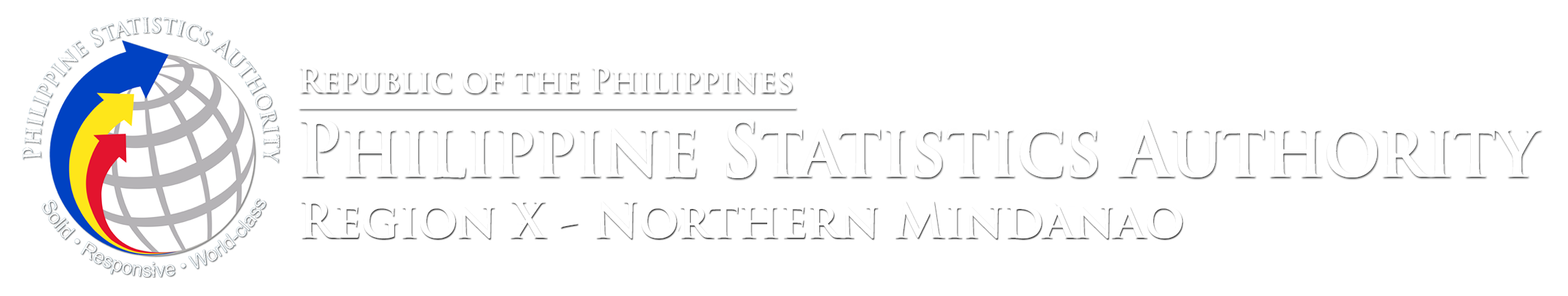
The inflation rate in the province of Camiguin in September increased to 5.8 percent, up from 4.4 percent in August. This brings the province’s year-to-date inflation to 7.0 percent. (Table A and Figure 1)
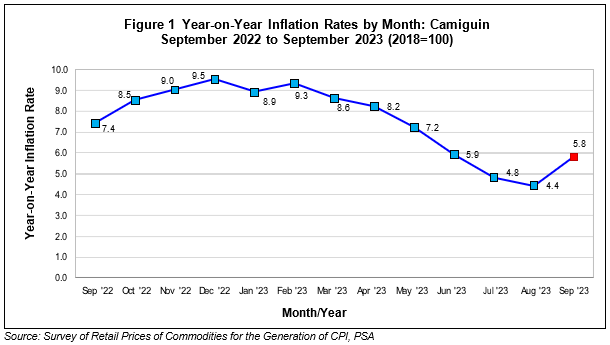
All five provinces across the Northern Mindanao Region experienced inflation increase in September 2023. The province of Lanao del Norte had the highest inflation rate, and also the highest increase among five provinces, as it recorded 9.1 percent in September 2023, which was up by 2.5 percentage points from 6.6 percent in August 2023. Meanwhile, the province of Misamis Occidental had the lowest inflation in the region, which recorded 5.3 percent in September 2023, although it was also higher during the month of August 2023 at 4.5 percent, up by 0.8 percentage points.
The provinces of Bukidnon, Misamis Oriental, and Camiguin also recorded higher inflation rates in September 2023 at 8.7 percent, 7.3 percent, and 5.8 percent respectively, higher than their posted inflation rates during the month of August 2023 at 6.1 percent, 5.5 percent, and 4.4 percent, accordingly.
Figure 2 presents the annual inflation rates of the provinces in Region X in September 2023.
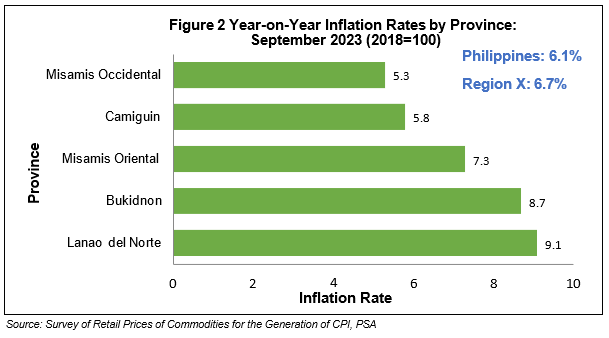
The higher inflation in the province was mainly brought about by the higher annual increase in food and non-alcoholic beverages at 11.5 percent in September 2023 from 7.2 percent in August 2023, or 4.3 percentage points increase during the month. Moreover, the indices of the following groups recorded higher annual increases during the month of September 2023:
• Alcoholic beverages and tobacco, 11.3 percent, from 9.3 percent;
• Furnishings, household equipment and routine household maintenance, 2.4 percent, from 2.1 percent;
• Health, -1.2 percent, from -1.7 percent;
• Transport, -5.4 percent, from -6.6 percent; and
• Recreation, sports, and culture, 2.9 percent, from 1.9 percent;
In contrast, lower inflation rates were noted in the indices of clothing and footwear at 0.1 percent, housing, water, electricity, gas and other fuels at 3.7 percent, restaurant and accommodation services at 3.7 percent, and personal care, and miscellaneous goods and services at 3.7 percent.
The information and communication had retained its recorded rate in August 2023 at 0.4 percent, while the financial and education services indices recorded a zero percent annual inflation rate in September 2023. (See Table 1)
Table 1 Year-on-Year Inflation Rates by Commodity Group:
Camiguin (2018 = 100)
The acceleration of food inflation in September 2023 was mainly caused by the higher inflation for rice which recorded a double-digit inflation rate of 20.6 percent during the month, from 8.1 percent in August 2023. This was followed by fish and other seafood with an inflation rate of 10.8 percent during the month from 2.0 percent inflation rate in August 2023. In addition, faster annual growth was noted in milk, other dairy products and eggs at 5.3 percent in September 3034 from 2.0 percent in the previous month. Further, higher annual increase was noted in the following food commodity groups: oils and fats (4.3%), fruits and nuts (5.0%), and ready made food and other food products n.e.c (2.8%).
On the other hand, the indices of for the rest of the food groups had slower annual increases during the month of September 2023.
(SGD)FRANCISCO C. GALAGAR JR.
Chief Statistical Specialist
Technical Notes
This Special Release presents the results of the Survey of Retail Prices of Commodities and Services for the Generation of Consumer Price Index (CPI) conducted in September 2023.
CPI
The CPI is an indicator of the change in the average retail prices of a fixed basket of goods and services commonly purchased by households for their day-to-day consumption relative to a base year.
Uses of the CPI
As an indicator, the CPI is most widely used in the calculation of the inflation rate and purchasing power of the peso. It is a major statistical series used for economic analysis and as monitoring indicator of government economic policy.
The CPI is also used as a deflator to express value series in real terms, which is, measuring the change in actual volume of transactions by removing the effects of price changes. Another major importance of the CPI is its use as basis to adjust wages in labor management contracts as well as pensions and retirement benefits. The CPI also serves as inputs in wage adjustments through the collective bargaining agreements.
Components of the CPI
a. Base Period
This is a reference date or simply a convenient benchmark to which a continuous series of index numbers can be related. Since the CPI measures the average changes in the retail prices of a fixed basket of goods, it is necessary to compare the movement in previous years back to a reference date at which the index is taken as equal to 100.
The present series uses the 2018 as the base year. The year 2018 was chosen as the base year because it is the year when the Family Income and Expenditure Survey (FIES) was conducted. The FIES is the basis of the CPI weights.
b. Market Basket
Market basket refers to a sample of thousands of varieties of goods purchased for consumption and services availed by the households in the country. It was selected to represent the composite price behavior of all goods and services purchased by the consumers.
c. Weighting System
The weighting system is a desirable system that considers the relevance of the components of the index. For the CPI, the weighting pattern uses the expenditures on various consumer items purchased by households as a proportion to total expenditures.
d. Geographic Coverage
CPI values are computed at the national, regional, and provincial levels, and for selected cities. A separate CPI for NCR is also computed.
e. Classification Standards
The 2012-based CPI series is the first in the series that used the 1999 United Nations Classification of the Individual Consumption According to Purpose (COICOP) in determining the commodity groupings of the items and services included in the market basket. The 2018-based CPI also follows the 2015 Philippine Standard Geographic Classification codes.
Inflation Rate
The inflation rate (IR) is the annual or monthly rate of change of the CPI in percent. It is interpreted in terms of declining purchasing power of money.