The volume of production of selected major crops in Northern Mindanao reached 10.267 million metric tons (MT) in 2021, an 8.5 percent increase from its volume of production in 2020. (Table 1 and Figure 1)
Table 1. Volume of Production of Selected Major Crops by Crop Group,
Northern Mindanao: 2020 and 2021 (In metric tons)
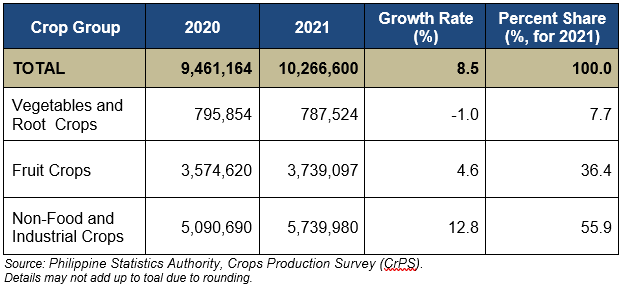
The total production of selected vegetables and root crops registered at 0.788 million MT, a 1.0 percent decrease from 0.796 million MT production in 2020. On the other hand, selected major fruit crops recorded a production of 3.739 million MT, equivalent to 4.6 percent increase from 3.575 million MT production posted in the previous year. Further, production of non-food and industrial crops in the region reached 5.740 million MT, an increase of 12.8 percent from 5.091 million MT production in 2020. (Table 1 and Figure 1)
In terms of volume, non-food and industrial crops posted a production gain of 649,290 metric tons while increase of fruit crops production was at 164,476 metric tons.
Among the three crop groups, non-food and industrial crops dominate with 55.9 percent share to total production, followed by fruit crops at 36.4 percent.
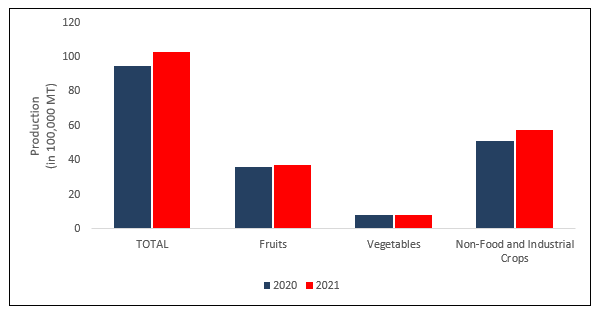
Figure 1. Selected Major Crops Production by Crop Group, Northern Mindanao: 2020 & 2021 (In 100,000 metric tons)
MAJOR FRUIT CROPS
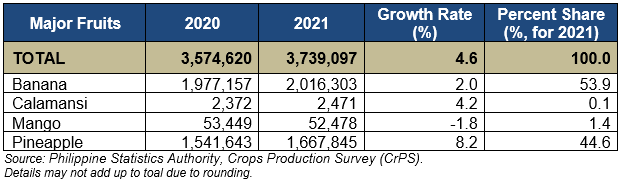
Among the major fruit crops produced, pineapple recorded the highest increase in production at 8.2 percent, followed by calamansi at 4.2 percent, and banana at 2.0 percent. On the other hand, mango recorded a 1.8 percent decrease in production. (Table 2)
In terms of volume, pineapple recorded the biggest increase in production at 126,202 meteric tons, followed by banana at 39,146 metric tons.
Banana accounted for 53.9 percent of the total production of major fruit crops in the region. Pineapple (1.668 million MT) ranked second with 44.6 percent share. Calamansi and mango had a combine share of 1.5 percent.
Table 2. Volume of Production of Selected Major Fruit Crops, Northern Mindanao: 2020 and 2021 (In metric tons)
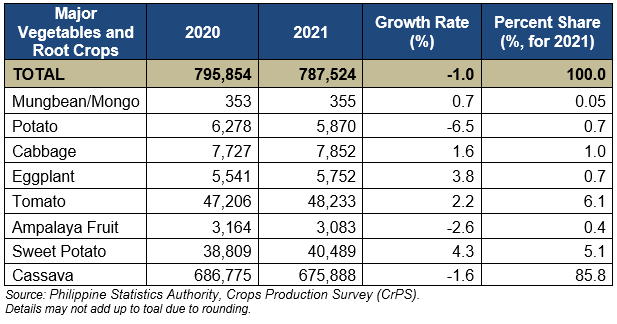
MAJOR VEGETABLES AND ROOT CROPS
Among the major vegetables and root crops, sweet potato recorded the highest growth at 4.3 percent, followed by eggplant which grew by 3.8 percent. All other selected major vegetables and root crops had an increase in production except for potato, ampalaya fruit, and cassava. (Table 3)
In terms of volume, cassava posted the biggest loss in production at 10,887 metric tons, while sweet potato (1,680 MT) registered the biggest gain in production, followed by tomato (1,028 MT).
Within the region, cassava (85.8% or 675,888 MT) accounted for the biggest share of the total production of major vegetables and root crops in the region.
Table 3. Volume of Production of Selected Major Vegetables and Rootcrops,
Northern Mindanao: 2020 and 2021 (In metric tons)
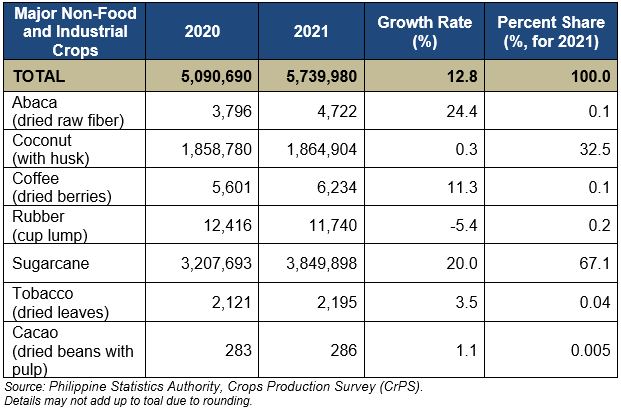
MAJOR NON-FOOD AND INDUSTRIAL CROPS
Among major non-food and industrial crops, abaca (dried raw fiber) posted the highest growth at 24.4 percent, followed by sugarcane at 20.0 percent and coffee (dried berries) at 11.3 percent. All other seleced major non-food and industrial crops had an increase in production except for rubber (cup lump) which had a reduction in its production at 5.4 percent.
In terms of volume, sugarcane posted the biggest gain in production at 642,205 metric tons, followed by coconut (with husk) at 6,124 metric tons.
Sugarcane accounted for 67.1 percent of the total regional production for selected non-food and industrial crops, while coconut (with husk) ranked second, accounting for 32.5 percent share. (Table 4)
TECHNICAL NOTES
Crops Production Survey
The Crops Production Survey (CrPS) aims to generate basic production statistics for crops other than palay and corn at the national, regional and provincial levels. It covers more than 200 crops of which 19 are considered major crops. This survey is undertaken nationwide on a quarterly basis.
Crop Production is the quantity produced and actually harvested for a particular crop during the reference period. It includes those harvested but damaged, stolen, given away, consumed, given as harvesters’ shares, reserved etc. Excluded are those produced but not harvested due to low price, lack of demand and force majeure or fortuitous events, etc.
Industrial Crops are crops that are used as inputs to other industries.
Major Crops refers to the top 19 crops in the Philippines, other than palay and corn which collectively account for more than 60 percent of the total volume of crop production. These include coconut, sugarcane, banana, pineapple, coffee, mango, tobacco, abaca, peanut, mongo, cassava, sweet potato, tomato, garlic, onion, cabbage, eggplant, calamansi and rubber.
Non-Food Crops are crops other than those used for food consumption. These are crops growth for their aesthetic values such as ornamental plants and cut-flowers. These also include agriculture-derived products such as rice hay and coconut leaves.
Root Crops are crops with well-developed underground edible roots. They are classified into roots and tubers. Roots, which are more starchy and rich in carbohydrates, include gabi, ubi and white potato. Tubers include beets, radish, carrots and turnips.
Vegetable Crops are mostly temporary crops which are either classified agronomically as such or based on purpose for which they are used, like jackfruit which on its young stage, is classified as vegetable.
(Sgd.) JANITH C. AVES, CE, DM (Chief Statistical Specialist) Officer-in-Charge